-
Glyphosate is broad-spectrum systemic herbicide that strongly inhibit class-1 EPSP synthase an important enzyme involved in aromatic amino acid synthesis in plants
-
Quality: the transgenic crops are not only herbicide tolerance but also enhance yield
Enhanced efficacy: No crop injury even at high dose of glyphosate
Cost advantage: More efficient alternate to the existing technology
Shelf life: Transgenic crops can be propagated forever
Ease of use: Like any other crop seeds 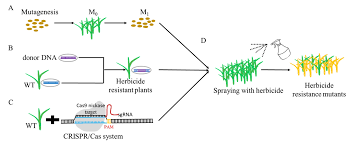
- 7. Developing glyphosate resistant transgenic crop plants using class-1 EPSP synthase
-
Direct use to farmers for weed control in the agriculture. Agri-Biotech companies for developing transgenic crops for weed management
- Indian Patent application No 202511009070
- India
-
The class-1 EPSP synthase present in crop plants is very sensitive to the herbicide glyphosate, currently the glyphosate resistant class-II EPSP synthase encoding gene from pathogenic Agrobacterium CP4 bacterial strain was used for transgenic overexpression in crop plants for glyphosate tolerance. We engineered glyphosate resistant Class-I EPSP synthase encoding gene whose overexpression has several advantages in addition to the glyphosate tolerance
-
Indian Patent application No 202511009070
- ICGEB New Delhi, India
- SANKARARAO GANTA
- Sankara.Ganta@icgeb.org
- Dr. M.K. Reddy
- kodandarami.reddy@icgeb.org
